Quick Summary
Click here for Price and Turnaround Time
Phenotype: Goats affected by G6-Sulfatase deficiency exhibit delayed motor development, growth retardation, and early death.
Mode of Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Alleles: N = Normal/Unaffected, G = G6-Sulfatase deficiency
Breeds appropriate for testing: Nubian and breeds derived from Nubian stock
Explanation of Results:
- Goats with N/N genotype will not have G6-Sulfatase deficiency and cannot transmit this G6-Sulfatase deficiency variant to their off spring.
- Goats with N/G genotype will not be affected by G6-Sulfatase deficiency, but are carriers. They may transmit this G6-Sulfatase deficiency variant to 50% of their offspring. Matings between two carriers are predicted to produce 25% G6-Sulfatase deficiency-affected kids.
- Goats with G/G genotype will have G6-Sulfatase deficiency, a condition leading to delayed development and early death.
Sample Collection
Most goat DNA tests offered by the VGL are carried out using 20-40 hairs with roots.
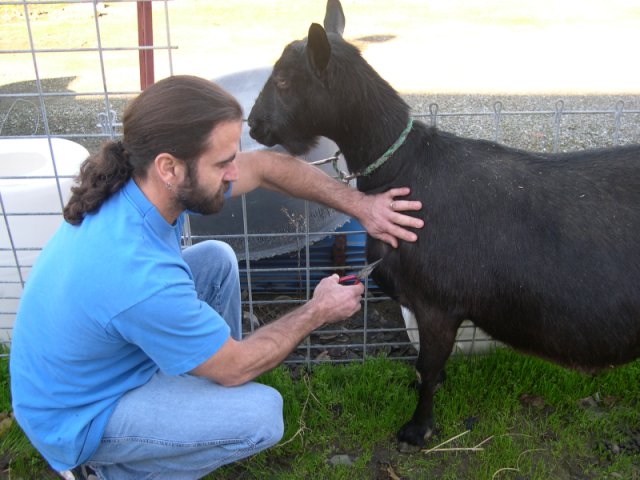
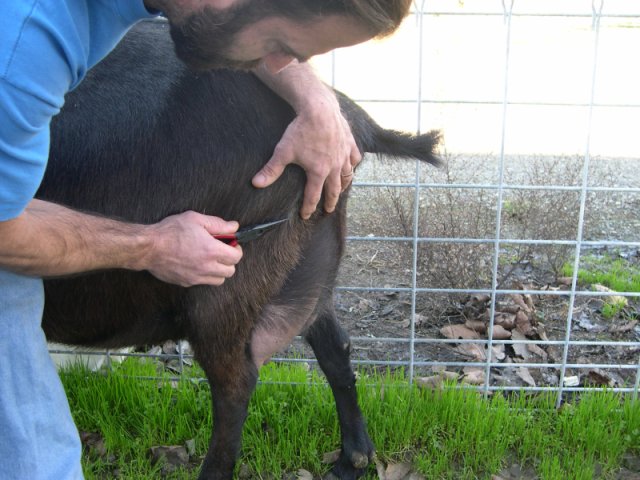
Hair root from coarse, longer hair often found over withers, chest, rump, tail, back of hind leg, poll, or fetlock is the preferred sample type for goats.
Instructions
1. Clean (use comb if possible) by removing all loose hair and foreign matter.
2. Use fingers or pliers to grasp approximately 8-10 hairs close to the skin and pull. Pull (do NOT cut) hair strands. Examine the end of hair strands for presence of root bulbs. Hair roots are necessary for DNA testing. If the majority of hair strands lack the root bulbs, discard hair and start again.
3. Repeat until you have approximately 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached.
4. Place the 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached in the envelope and seal with the animal’s ID written on the envelope.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 for each additional animal being sampled.
Note:
- Hair should be dry.
- If hair has excess dirt and debris, please brush out if possible before pulling hairs for sample.
- Do not cut the hair! The roots contain the DNA for testing.
- When sampling several animals in the same session, make sure that there are no hair strands in your hands to reduce the possibility of sample contamination. Clean hands and/or pliers if possible.
Examples
Sampling goat chest hair:

Sampling goat rump hair:

Sampling technique using pliers:
G6-Sulfatase deficiency is an inherited metabolic defect that occurs in Nubian goats and related crosses. A mutation in the G6-S gene renders the enzyme incapable of degrading complex polysaccharides known as heparin-sulfate glycosaminoglycans (HS-GAGs) which then abnormally accumulate in tissues such as the central nervous system and viscera. Clinically, affected goats exhibit delayed motor development, growth retardation, and early death.
The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. Therefore, both sexes are equally affected and two copies of the defective gene must be present for signs of the disorder to be observed. Breeding two carrier goats, which are normal but each possesses a single copy of the mutation, is predicted to produce 25% affected offspring.
Breeders can use results from this test as a tool for selection of mating pairs to avoid producing affected kids. The test is recommended for Nubian goats and breeds derived from Nubian stock.
