Quick Summary
Click here for Price and Turnaround Time
A freemartin is defined as a female that is born as a twin with a male and is sterile as a result of exposure to masculinizing hormones. A connection between the two fetal circulatory systems develops early in gestation (anastomosis) and leads to the exchange of blood between the fetuses. Exposure to male hormones leads to underdevelopment of the female's reproductive tract.
Sample Collection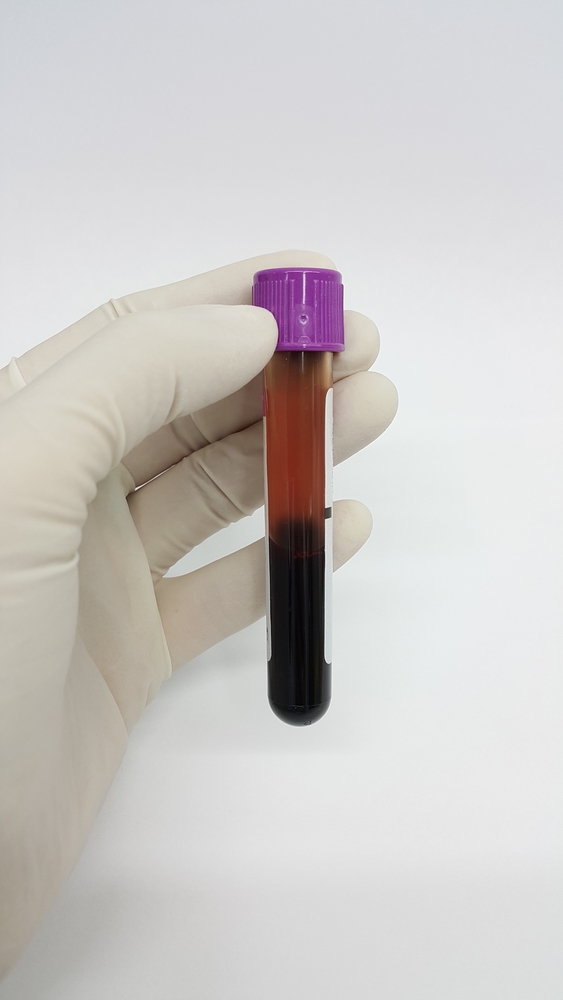
The freemartin test requires a blood sample.
VGL requires 3 mL of whole blood in an EDTA purple top tube for testing
- Label the tube with the animal's name exactly as it appears on the order
- Place the tube in a plastic bag and pack the blood well enough to withstand the rigors of shipping - we cannot test a broken sample
- Please include an ice pack to keep the sample cool while in transit
- We highly recommend sending the sample overnight through FedEx or UPS at the beginning of the week as we do not have staff on the weekend to process samples
For samples mailed through FedEx/UPS/DHL etc:
Veterinary Genetics Laboratory
University of California Davis
Old Davis Road
Davis, CA 95616
Incidence of freemartinism in goats is generally low (less than 1%); increased risk has been observed when litter sizes are four or more. Other intersex phenotypes in goats can result from effects of the polled gene. This DNA test that detects presence of Y-chromosome confirms chimerism in the blood of females suspect of being freemartins.
