Quick Summary
Click here for Price and Turnaround Time
Phenotype: The albino mutation produces a white coat with blue eyes.
Mode of Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Alleles: N = Normal/non-albino, A = Albino
Breeds appropriate for testing: Tonkinese, Siamese, blue-eyed white cats of other breeds
Explanation of Results:
- Cats with N/N genoytpe will not be albino and cannot transmit this albino variant to their offspring.
- Cats with A/N genotype will not be albino, but are carriers. They will transmit this albino variant to 50% of their offspring. Matings between two carriers are predicted to produce 25% albino kittens.
- Cats with A/A genotype will be albino, and will transmit this albino variant to all of their offspring. Matings between two A/A genotype cats are predicted to produce all albino kittens.
Cat DNA tests are carried out using cells brushed from your cat's cheeks and gums using household cotton swabs.
The cat DNA submission form with instructions and a place to tape the cotton swabs is sent to you via email after you place an order, and can be printed from your home computer. DNA test kits are no longer mailed.
Instructions
Step-By-Step:
1.
 Purchase regular household cotton swabs for cat DNA collection (the cotton swabs can be purchased at a pharmacy or drug store)
Purchase regular household cotton swabs for cat DNA collection (the cotton swabs can be purchased at a pharmacy or drug store)
2.

Make sure the cat has not had anything to eat or drink for at least 1 hour prior to collecting sample.
When swabbing kittens, isolate each kitten from the mother, littermates and any shared toys for 1 hour prior to swabbing. Kittens should not have nursed or eaten for 1 hour prior to collecting sample.
If collecting samples from more than one cat, make sure to sample one cat at a time and wash your hands before swabbing another cat.
3.
 Use both ends of the two cotton swabs for a total of four swabs.
Use both ends of the two cotton swabs for a total of four swabs.
4.
Place the cotton head of the swab between the cat’s gums and cheek and rub or rotate the swab back and forth for 15 seconds. Repeat with each cotton swab head, for a total of 4 swabs. We recommend swabbing a different area of the gums with each swab head.
5.
Wave the swab in the air for 10-15 seconds to air dry it before attaching it to the submission form.
6.
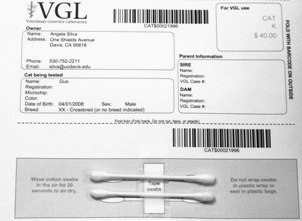 After swabbing the cheek and gums, tape the cotton swabs to the bar-coded submission form printed from your MyVGL account.
After swabbing the cheek and gums, tape the cotton swabs to the bar-coded submission form printed from your MyVGL account.
ATTENTION:
- Do not collect saliva/drool – the key to obtaining a good sample is getting cheek cells on the swab.
- Do not rub swab on the cat’s tongue or teeth – this will result in poor quality sample.
- Do not collect a sample from a kitten that has recently nursed – the mother’s genetic material can rub off on the kitten’s mouth and contaminate the sample.
Feline albinism is a rare inherited condition characterized by a lack of pigment resulting in cats with a white coat and blue eyes.
Two mutations in the Tyrosinase (TYR) gene produce the Burmese (sepia), Siamese, and mink colorpoint coat and eye color phenotypes in cats. A rare mutation in TYR (c.936delC) causes a shortened form of the TYR protein and produces an albino phenotype of a white coat with blue eyes. The albino mutation is recessive to the Burmese (cb) and Siamese(cs) mutations following the allelic series C>cb=cs>ca.
