Quick Summary
Click here for Price and Turnaround Time
Phenotype: Cholesterol deficiency (CD) affects lipid metabolism and causes young calves to die, usually within 3 weeks to 6 months of age, as a consequence of chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive. Affected calves show very low levels of cholesterol (severe hypocholesterolemia).
Mode of Inheritance: Autosomal recessive
Alleles: N = Normal/Unaffected, CD = Cholesterol deficiency
Breeds appropriate for testing: Holstein, Holstein crosses
Explanation of Results:
- Cattle with N/N genotype will not be affected by cholesterol deficiency. They cannot transmit this cholesterol deficiency variant to their offspring.
- Cattle with N/CD genotype are not expected to show clinical signs of cholesterol deficiency, but are carriers. They will transmit this cholesterol deficiency variant to 50% of their offspring. Matings between two carriers result in a 25% chance of producing a calf with cholesterol deficiency.
- Cattle with CD/CD genotype will be affected by cholesterol deficiency, a lethal condition.
Sample Collection
Most of the cattle DNA tests offered by the VGL are carried out using cells from the roots of a hair sample (roughly 20-40 hairs).
Hair samples should be taken from the switch of the tail, the poll, or the neck.
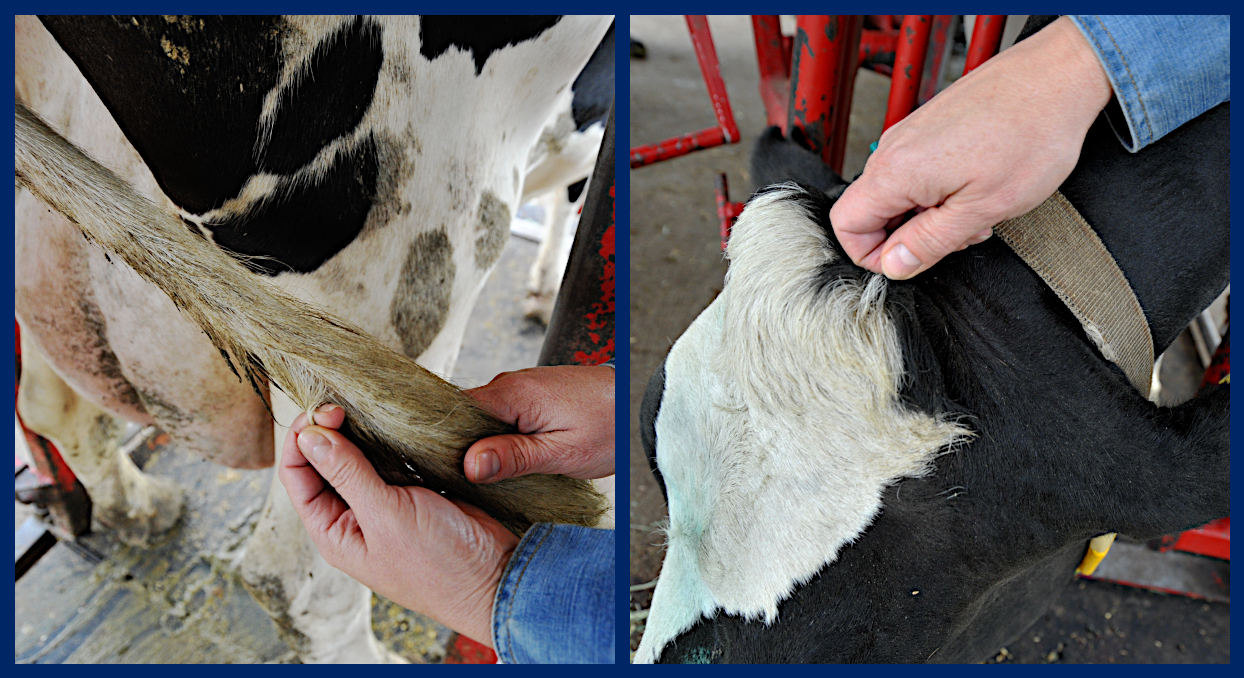
1. Clean (use comb if possible) tail switch, poll, or neck by removing all loose hair and foreign matter.
2. Use fingers or pliers to grasp approximately 8-10 hairs close to the skin and pull. Pull (do NOT cut) hair strands. Examine the end of hair strands for presence of root bulbs. Hair roots are necessary for DNA testing. If the majority of hair strands lack the root bulbs, discard hair and start again.
3. Repeat until you have approximately 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached.
4. Place the 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached in the envelope and seal with the animal’s ID written on the envelope. If hairs are long they can be taped to the submission form. Do not tape the roots.
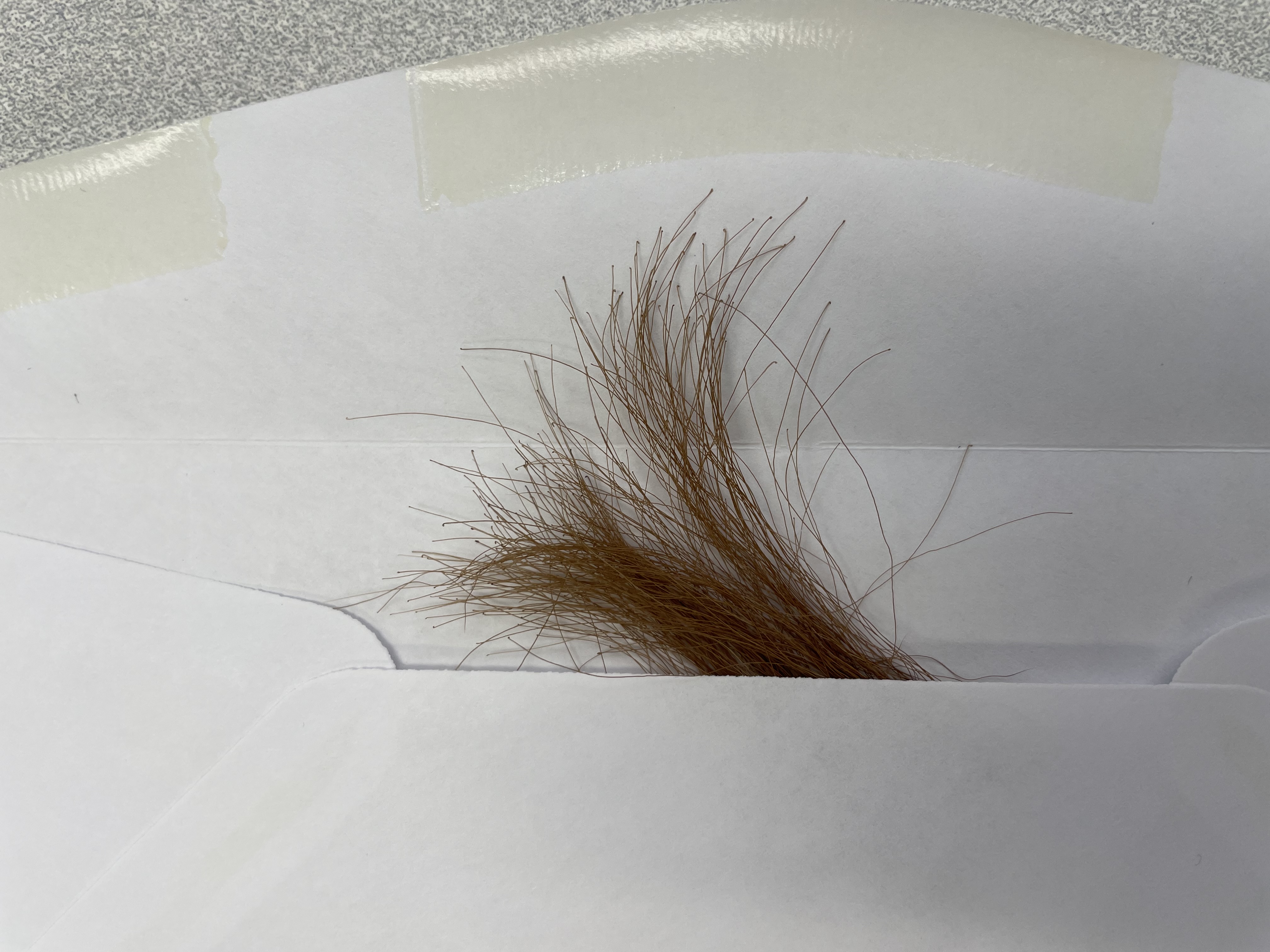

5. Repeat steps 1-4 for each additional animal being sampled.
Note:
- Hair should be dry.
- If hair has excess dirt and debris, please brush out if possible before pulling hairs for sample.
- Do not cut the hair! The roots contain the DNA for testing.
- When sampling several animals in the same session, make sure that there are no hair strands in your hands to reduce the possibility of sample contamination. Clean hands and/or pliers if possible.
Cholesterol deficiency (CD) is a recessive genetic disorder in Holstein cattle that affects lipid metabolism and causes young calves to die, usually within 3 weeks to 6 months of age, as a consequence of chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive. Affected calves show very low levels of cholesterol (severe hypocholesterolemia). The genetic defect traces back to bull Maughlin Storm born in 1991.
Molecular analyses identified the mutation responsible for CD as a 1.3Kb insertion of a transposable LTR element (ERV2-1) in the coding sequence of the apolipoprotein B (APOB) gene that renders the APOB protein non-functional. The APOB protein is a key component in a system responsible for transporting fat molecules, including cholesterol, around the body and into cells. Carriers of CD appear to be normal and show no clinical signs of malabsorption despite a reduced level of cholesterol when compared to non-carriers. A DNA diagnostic test for the APOB mutation has been developed by researchers in Switzerland to determine whether animals are free of the mutation, are CD-carriers (1 copy of the mutation) or CD-affected (2 copies of the mutation).
Breeders can use results from this test from the VGL, which is specific for the Holstein CD mutation, as a tool for selection of mating pairs to avoid producing affected calves.
Other Holstein breed-specific tests offered by the VGL:
