Quick Summary

Click here for Price and Turnaround Time
Phenotypes:
- Dominant black: Holstein cattle with dominant black are black and white.
- Black/Red: The Black/Red variant results in red color at birth which changes to black at a young age, usually by 3-6 months.
- Wild type red: Wild Type red produces cattle with red and white coloration that may appear darker towards the extremities of the body, especially as the animal ages.
- Recessive red: Cattle with two copies of the recessive red allele are red in color.
Mode of Inheritance: Autosomal recessive, order of dominance is ED > E BR > E+ > e
Alleles:
ED = Dominant black
EBR = Black/Red (Telstar)
E+ = Wild type
e = Recessive red
Breeds appropriate for testing: Holstein
Explanation of Results:
- Cattle with ED/ED genotype will be black and white and cannot produce true red offspring.† They will transmit this dominant black variant to all of their offspring.
- Cattle with ED/EBR, ED/E+, and ED/e genotypes will be black and white and are carriers of their respective less-dominant variants. Matings between two carriers of the same recessive variant (e.g. ED/e x ED/e) result in a 25% chance of producing a calf with that recessive coloration (e.g. ED/e x ED/e has a 25% chance of producing a red calf).†
- Cattle with EBR/EBR genotype will be Black/Red and cannot produce true red offspring.† They will transmit this Black/Red variant to all of their offspring.
- Cattle with EBR/E+ and EBR/e will be Black/Red and carriers of their respective less-dominant variants. Matings between two carriers of the same recessive allele (e.g. EBR/E+ x EBR/E+) result in a 25% chance of producing a calf with that recessive coloration (e.g. EBR/E+ x EBR/E+ has a 25% chance of producing a Wild type-colored calf).†
- Cattle with E+/E+ genotype will be Wild type red and white. They will transmit this Wild type variant to all of their offspring.
- Cattle with E+/e genotype will be Wild type red and white and carriers of recessive red. They will transmit this recessive red variant to 50% of their offspring. Matings between two carriers of recessive red result in a 25% chance of producing a calf with recessive red coloration.
- Cattle with e/e genotype will be recessive red and white. All calves produced from matings with other e/e genotype cattle will have recessive red base coloration.
†In the absence of the Dominant Red mutation. Holsteins with the Dominant Red variant will be red and white regardless of MC1R genotype. See Dominant Red test for more information.
Sample Collection
Most of the cattle DNA tests offered by the VGL are carried out using cells from the roots of a hair sample (roughly 20-40 hairs).
Hair samples should be taken from the switch of the tail, the poll, or the neck.
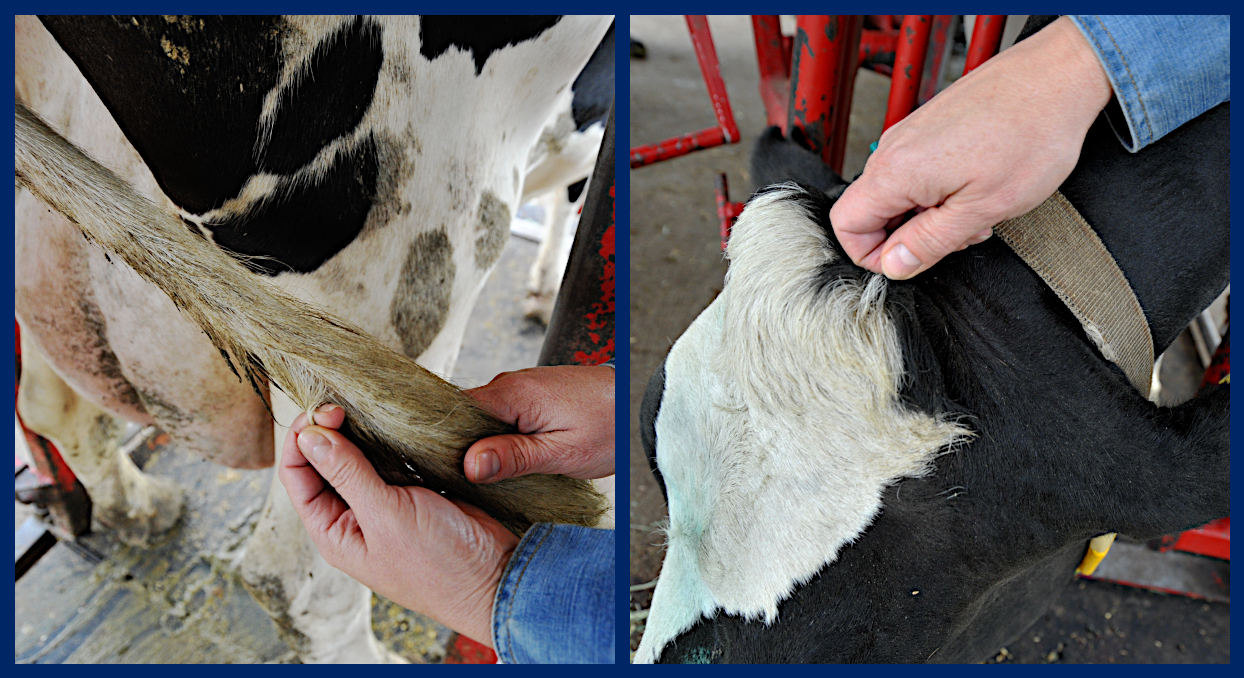
1. Clean (use comb if possible) tail switch, poll, or neck by removing all loose hair and foreign matter.
2. Use fingers or pliers to grasp approximately 8-10 hairs close to the skin and pull. Pull (do NOT cut) hair strands. Examine the end of hair strands for presence of root bulbs. Hair roots are necessary for DNA testing. If the majority of hair strands lack the root bulbs, discard hair and start again.
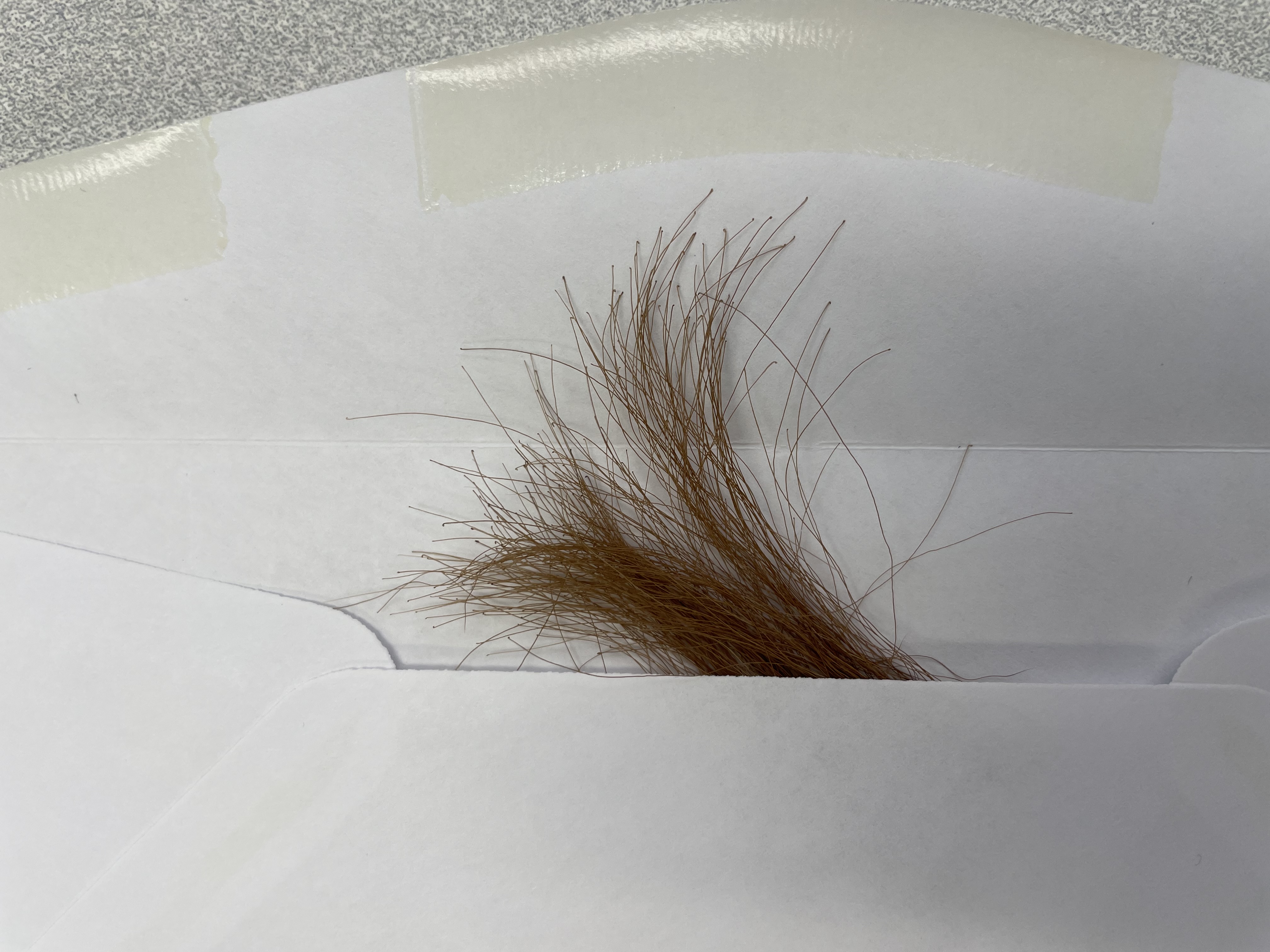
3. Repeat until you have approximately 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached.
4. Place the 20-40 hairs with root follicles attached in the envelope and seal with the animal’s ID written on the envelope. If hairs are long they can be taped to the submission form. Do not tape the roots.

5. Repeat steps 1-4 for each additional animal being sampled.
Note:
- Hair should be dry.
- If hair has excess dirt and debris, please brush out if possible before pulling hairs for sample.
- Do not cut the hair! The roots contain the DNA for testing.
- When sampling several animals in the same session, make sure that there are no hair strands in your hands to reduce the possibility of sample contamination. Clean hands and/or pliers if possible.
The Melanocortin-1 Receptor gene (MC1R), also called Extension (E), controls black and red pigment production in cattle. Holstein cattle have another gene, Dominant Red, which overrides MC1R and produces dominant red pigment. Both the Dominant Red test and this Holstein-specific MC1R test help Holstein breeders select for their preferred color variants.
The four alleles of the MC1R gene are dominant black (ED), Black/Red (EBR), wild type red (E+), and recessive red (e). Dominant black (ED) is dominant to the other three alleles, and animals with ED are black and white. Black/Red, also known as Telstar, (EBR), results in red color at birth which changes to black at a young age, usually by 3-6 months. Wild type red (E+) produces cattle with red and white coloration that may appear darker towards the extremities of the body, especially as the animal ages. Two copies of the recessive red (e) allele result in red color. The order of dominance is ED>EBR>E+>e.
Other Holstein breed-specific tests offered by the VGL:
